
Executive & Strategy
FactoryKPI Executive
KPI Dashboard with Multi-plant analytics and comparisons
Problem Solving
SolvoNext-PDCA
A Smarter Problem Solving and Project Management Software based on deming and Toyota's PDCA - Plan, Do, Check, Act Method.
Qualitygram
A Unique Mobile and Web Software that helps Manage and Solve Problems Faster with Improved Team Communication.
SolvoNext-NCR CAPA
Digitize your NCR & CAPA process and Reduce Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ).

Skills Development vs. Training Understanding the Differences
October 8, 2024
In manufacturing, two terms often used interchangeably are skills development and training. While they are closely related, they serve different purposes in shaping a more capable, efficient workforce. To achieve operational excellence, manufacturers must distinguish between the two and invest in both. In this blog, we'll explore the key differences between skills development and training in manufacturing, their unique roles, and how each contributes to a more productive and dynamic workforce.
Training in Manufacturing
Training refers to the structured, short-term process of teaching employees the specific tasks, procedures, and rules necessary to perform their jobs effectively. In the manufacturing environment, training typically focuses on equipping workers with the practical skills required to operate machinery, follow safety protocols, adhere to standardized work instructions, and complete production tasks with accuracy.
Training is often conducted when an employee is new to the job, when new equipment is introduced, or when processes change. According to the World Economic Forum, globally, only one-third of companies identify a robust training dispensation as attractive to prospective employees, this figure rises to 40% among SMEs.
Examples of Training in Manufacturing:
- Safety Training: Teaching workers how to follow OSHA safety guidelines to prevent workplace accidents.
- Machine Operation Training: Showing employees how to properly operate new machines such as CNC machines, assembly robots, or forklifts.
- Process-Specific Training: Training employees on specific processes like assembly line procedures or quality inspection methods.
Who Benefits from Training?
- Workers: Gain the knowledge they need to perform tasks correctly and safely.
- Managers: Can trust that their teams are following proper procedures and meeting standards.
- Companies: Benefit from increased productivity, fewer errors, and higher safety compliance.
Mentorship and networking play crucial roles in accelerating career growth and skills development, especially in quality management roles. Learn more about how these elements contribute to success.
When to Apply Training in Manufacturing
- Onboarding New Employees: Training is crucial during the onboarding of new employees who are unfamiliar with the specific machinery, tools, and processes used in manufacturing. This ensures that they quickly learn how to operate equipment properly and adhere to the company’s standards. By providing structured, hands-on training, new hires can integrate more smoothly into the production process, minimizing mistakes and improving their confidence in their roles.
- Introducing New Equipment or Technology: When new machinery or technology is introduced to the manufacturing floor, it’s essential to train workers on how to operate the new systems effectively. This helps them understand new functionalities, potential risks, and how to maintain the equipment. Proper training on new technology ensures that productivity remains high, while reducing the likelihood of breakdowns or errors due to unfamiliarity.
- Implementing New Safety Regulations: Training is necessary when new safety regulations or procedures are introduced. Workers need to be informed about these changes to ensure compliance and maintain a safe working environment. By familiarizing employees with updated safety protocols, such as OSHA guidelines or industry-specific standards, manufacturers can reduce accidents, avoid penalties, and ensure a safe, compliant workspace.
- Correcting Specific Deficiencies in Performance: Training is also essential for addressing performance gaps, such as quality control issues or inefficiencies in production. When employees underperform due to skill deficits, targeted training helps correct these deficiencies by reinforcing proper techniques, increasing understanding, and improving overall performance. This ensures that workers meet quality and productivity standards, reducing defects and rework in the long run.
Skills Development in Manufacturing
Skills development is a broader, long-term process focused on enhancing an employee's overall capabilities beyond the immediate demands of their job. It involves continuous learning, the acquisition of advanced technical skills, and the refinement of soft skills like problem-solving, critical thinking, leadership, and communication. Unlike training, skills development is more forward-thinking, preparing employees for future challenges, career progression, and adaptability in a rapidly changing manufacturing landscape.
Skills development goes beyond the basics and delves into advanced competencies that enable workers to innovate, improve processes, and even step into leadership roles.
Examples of Skills Development in Manufacturing:
- Technical Upskilling: Providing courses on programming for automated systems, advanced machine maintenance, or CAD design.
- Leadership Development: Preparing workers for supervisory or management roles by honing their leadership and decision-making abilities.
- Problem-Solving Workshops: Teaching employees methodologies like Lean, Six Sigma, or root cause analysis to foster continuous improvement.
Who Benefits from Skills Development?
- Workers: Gain long-term career growth opportunities, new competencies, and increased job satisfaction.
- Managers: Develop stronger teams that are more capable of problem-solving, innovation, and leadership.
- Companies: Benefit from having a more adaptable, versatile workforce that contributes to continuous improvement and innovation.
When to Apply Skills Development in Manufacturing
Build a More Adaptable Workforce
Skills development is crucial for creating a workforce that can quickly adapt to new technologies, equipment, and processes. As manufacturing evolves with automation, AI, and advanced machinery, employees must be able to transition smoothly to new systems. Ongoing skills development ensures that workers remain flexible, can efficiently operate new tools, and minimize downtime during technological shifts, making them more resilient in a rapidly changing industry. As per the 2022 study by Deloitte reported that skilled workers are more likely to grow and develop by 98%.
Discover how manufacturers are addressing labor challenges with effective workforce training and skills development.
Equip Employees with Advanced Skills for Innovation
Developing employees' advanced technical skills allows them to contribute to innovation and continuous improvement. By investing in skills like data analysis, advanced machinery programming, or Lean Six Sigma methodologies, manufacturers empower workers to identify inefficiencies and implement solutions that enhance productivity and product quality. This approach fosters a proactive culture where employees are not just executing tasks but actively driving improvement initiatives. As per the 2022 study by Deloitte reported that skill based organizations are more likely to innovate by 52% and place talent effectively by 107%.
Develop Leadership Skills in Potential Supervisors
Skills development is essential for identifying and grooming future leaders within the company. Employees who show potential for supervisory or managerial roles benefit from leadership development programs that teach decision-making, team management, and strategic thinking. By cultivating leadership skills, manufacturers create a pipeline of capable leaders ready to take on greater responsibilities, ensuring continuity and strong leadership as the company grows.
Foster a Culture of Continuous Learning
Continuous skills development nurtures a learning culture where employees are motivated to expand their knowledge, take on new challenges, and embrace responsibility. This culture of growth not only improves individual performance but also contributes to the overall development of the company. Workers are more likely to innovate, take initiative, and contribute ideas when they feel empowered through ongoing learning and development opportunities, leading to a more dynamic and progressive manufacturing environment.
Key Differences Between Training and Skills Development
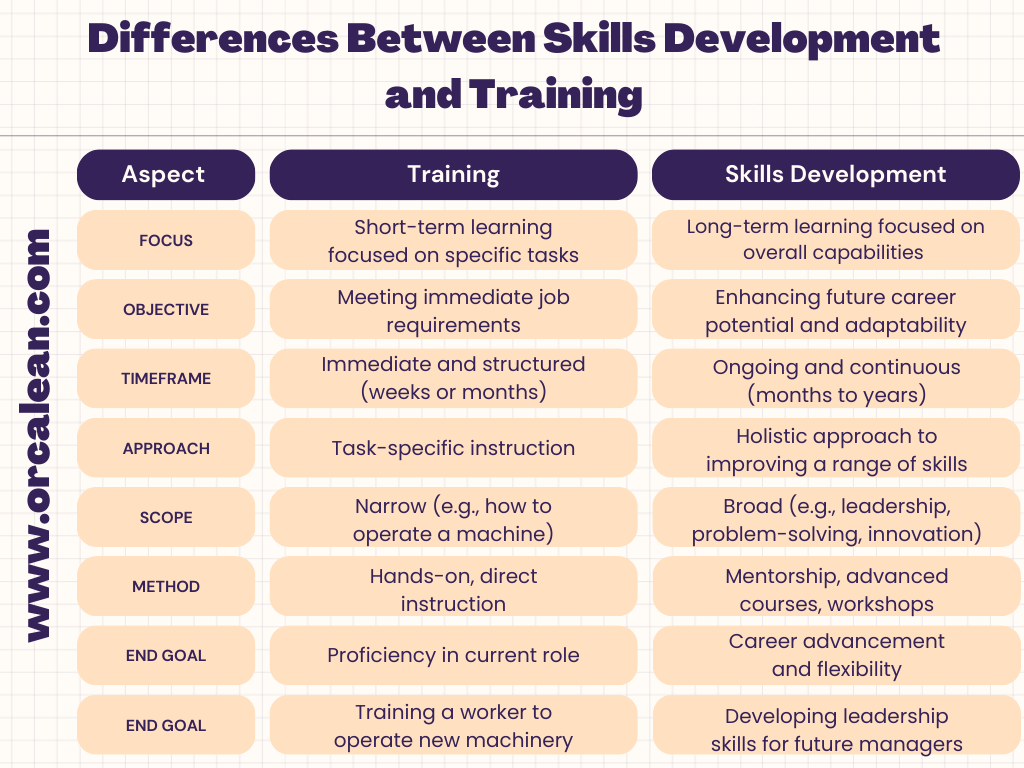
1. Timeframe
- Training: Typically short-term and focused on immediate job requirements. It addresses "how-to" tasks and operational basics.
- Skills Development: Long-term and focused on an employee’s growth and future adaptability. It’s about deepening knowledge and advancing capabilities.
2. Focus
- Training: The focus is on teaching specific tasks and procedures. It’s about ensuring that employees can perform their current roles efficiently.
- Skills Development: The focus is on overall career and personal growth. It’s about expanding a worker's skill set and preparing them for future roles and responsibilities.
3. Objective
- Training: The objective is to help employees meet the minimum requirements for performing their current job safely and correctly.
- Skills Development: The objective is to create a more versatile and skilled workforce capable of handling more complex tasks and adapting to change.
4. Methodology
- Training: Involves direct instruction, often with a hands-on component that focuses on operational procedures. Training is usually delivered through on-the-job learning or workshops.
- Skills Development: Involves a combination of mentoring, advanced education, continuous learning opportunities, and personal development initiatives. It may include certifications, courses, and self-directed learning.
The Intersection of Training and Skills Development
Although training and skills development serve different purposes, they are closely linked. Both are vital to creating a workforce that is not only competent in their current roles but also prepared to meet the demands of the future. Many companies are finding success by integrating these two concepts into a single, unified approach to employee growth.
According to the All Research Journal, improvements in skill, career, motivation, modernisation of work, and self and time management also significantly contribute to the organizational benefits. This work has demonstrated how the organizational improvement in the companies was influenced by employee and work practice improvements because of technical training.
As per the 2022 study by Deloitte , skill development improves the procossess to maximum efficiency by 49%.
For example, a company may offer initial machine operation training followed by continuous development programs in advanced maintenance and leadership. This approach ensures that employees are productive in the short term while continually advancing their skills for long-term success.
Conclusion
In manufacturing, both training and skills development are crucial for building a capable workforce. While training focuses on the immediate needs of the job, ensuring that workers know how to perform tasks safely and efficiently, skills development is about long-term growth and preparing employees for future roles. By understanding the differences and applying both approaches effectively, manufacturers can create a dynamic workforce that drives innovation, productivity, and long-term success.

Software Solutions for Manufacturing Excellence
Company
Social
Our Contact Info:
Email: contact@orcalean.com
Phone Number: 248 938 0375
Our Offices